Coagulants: what they are and how they work
Any water has impurities: natural, industrial or household water. Impurities are divided into suspended solids and colloids. Suspended solids are large, heavy particles that settle on their own and can be filtered or sedimented. Colloids are small particles that pass through a standard filter. They are equally charged, so they repel each other and do not settle - it is useless to sediment a liquid with colloids. To purify such water you need coagulation - collection of colloidal particles with the help of reagents - coagulants.
What are coagulants and what are they
Coagulants are reagents that stick colloidal particles into flakes. These flakes are already quite large and heavy, so the water after coagulation can be cleaned by mechanical means.
There are two types of coagulants: organic and inorganic. Organic are polyelectrolytes and polymers, which are divided into artificial and natural. Inorganic coagulants are mineral reagents, mostly iron and aluminum salts. Their main advantage is the price.
Compared to them, organic ones are more economical and efficient to use, because:
-
form less sludge, the sludge itself contains less liquid and is better dewatered - this reduces the cost of its removal and disposal;
-
do not change the pH - alkaline chemicals are minimized or not needed at all;
-
do not add aluminum and iron to the water - this simplifies the treatment step;
-
do not harm the environment;
-
they give higher rates of chemical reactions at lower doses and work faster.
Coagulants come in the form of powder in bags, solution in canisters and containers, paste in buckets or barrels. The solution is more convenient because it is ready to use. Powder must be diluted in water before use, but it is cheaper.
Coagulants Biomicrogels® are derived from agricultural products: apple and beet pulp, cellulose, starch
How coagulation works
It is a process when colloids under the influence of coagulants lose their charge and no longer repel each other on collision, but unite into groups and precipitate out - coagulate.
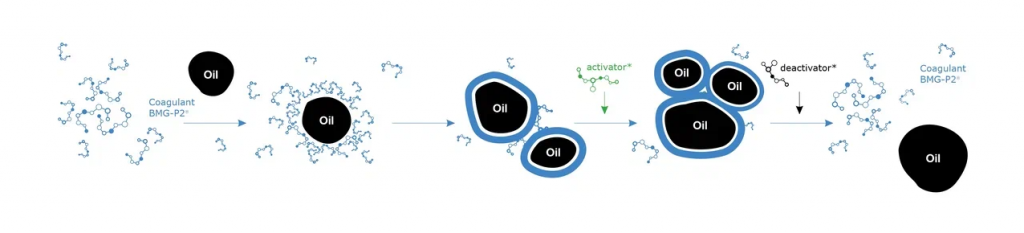
Coagulation using used coolant as an example: Coagulants group the oil particles, they settle, they are removed from the water and the water is purified
The benefits of coagulation
-
Reagents dissolve quickly, so no long stirring is required.
-
Quickly separates liquid and solid phase - colloids.
-
Extends the life of direct filtration filters.
-
Cheaper and easier to use than industrial ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis.
Coagulation as an example for cleaning water from coolants and petroleum products: BMG-P2 coagulant forms a sludge in less than a minute
Disadvantages of coagulation
-
Requires prior analysis of fluid contamination and cleaning requirements. Only then can the type of reagent be selected, a suitable dosage be calculated and strictly adhered to.
-
Forms sludge that needs to be sedimented, cleaned up, filtered.
-
Removes some of the suspended matter, but viruses and bacteria may remain in the water - a disadvantage for drinking water purification.
-
Needs additional equipment - this is a disadvantage for individuals who want to set up a system at home.
Where and how are coagulants used
They are used wherever there is a need to thicken substances, to settle suspended particles in the liquid. In the construction industry, they accelerate the setting of concrete, in medicine they are needed to increase blood clotting, in mining they are involved in the enrichment of minerals.
But the main area of application is water treatment. Coagulants are used in wastewater treatment plants, swimming pools, for drinking water preparation and for the treatment of industrial dirty water, e.g. from oil products.
The application of coagulants takes place in 4 steps:
-
Selection of the reagent and its dosage depending on the purpose of the liquid, its degree of contamination, temperature and treatment method.
-
Preparation of the solution and its introduction into the contaminated liquid.
-
Maintaining optimal conditions for the reaction: stirring, maintaining the correct temperature, pH.
-
Removal of sludge by means of sedimentation and water filtration.
In wastewater treatment plants, coagulation makes it cheaper to disinfect water and improves its quality - less chlorine is needed after coagulation, which means fewer toxic byproducts
Conclusion
Coagulation is an important step before water treatment that should not be skipped. For example, to purify a water-oil emulsion, it must first be separated into water and oil using coagulants. When treating drinking water, coagulants remove organic impurities that interfere with disinfection.
In industry, this process can be replaced by ultrafiltration, and in the domestic sphere by reverse osmosis. But both alternatives are considerably more expensive and more difficult to use. Therefore, coagulation remains the most profitable method for large volumes of water. It can be made even more efficient by adding flocculation. This is the bonding of coagulated flocs so that they become even larger, heavier and settle to the bottom faster. We'll talk more about this in our article on flocculants.




